Learn more about our impact
Learn more about our impact
- What we care about
- People
- Places
- Species
- Climate crisis
- Sustainability
- How we work
- Public policy
- Science
- Business
- Wildlife conservation
About WWF
WWF works to sustain the natural world for the benefit of people and wildlife, collaborating with partners from local to global levels in nearly 100 countries.
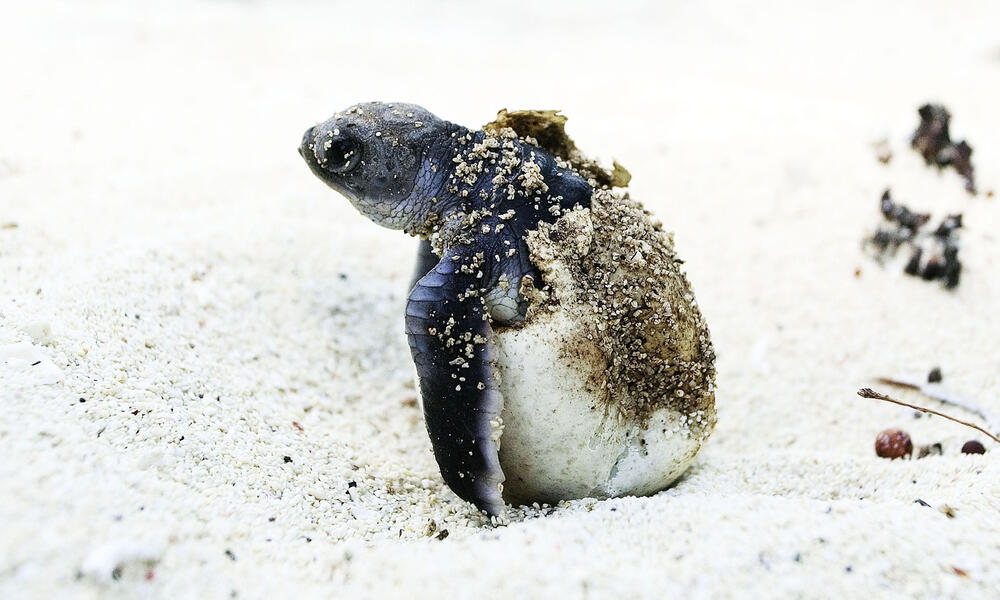
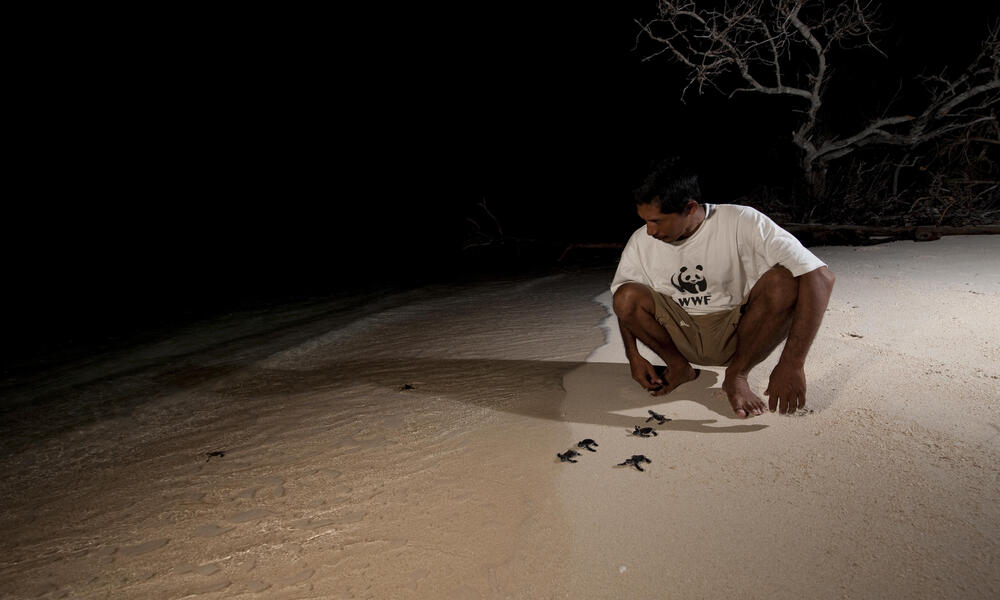






 Hawksbill Turtle
Hawksbill Turtle
 Loggerhead Turtle
Loggerhead Turtle
 Leatherback Turtle
Leatherback Turtle
 Olive Ridley Turtle
Olive Ridley Turtle
 Sea Turtle
Sea Turtle
 Vaquita
Vaquita
 Whale Shark
Whale Shark
 Dugong
Dugong
 Humphead Wrasse
Humphead Wrasse
 Pacific Salmon
Pacific Salmon
 Dolphins and Porpoises
Dolphins and Porpoises
 Whale
Whale
 Seals
Seals
 Sea Lions
Sea Lions
 Marine Iguana
Marine Iguana
 Tuna
Tuna
 Bluefin Tuna
Bluefin Tuna
 Sei Whale
Sei Whale
 Yellowfin Tuna
Yellowfin Tuna
 Skipjack Tuna
Skipjack Tuna
 Great White Shark
Great White Shark
 Albacore Tuna
Albacore Tuna
 Bigeye Tuna
Bigeye Tuna
 North Atlantic Right Whale
North Atlantic Right Whale
 Blue Whale
Blue Whale
 Fin Whale
Fin Whale
 Bowhead Whale
Bowhead Whale
 Gray Whale
Gray Whale
 Hector's Dolphin
Hector's Dolphin
 Galápagos Penguin
Galápagos Penguin
 Shark
Shark
 Polar Bear
Polar Bear
 Narwhal
Narwhal
 Beluga
Beluga
 African Wild Dog
African Wild Dog
 African Elephant
African Elephant
 Black Rhino
Black Rhino
 White Rhino
White Rhino
 Rhino
Rhino
 Giant Tortoise
Giant Tortoise